Safe Beta-Blockers: Best Options for Heart Health Without the Risks
When you need a beta-blocker, a class of medications that slow your heart rate and lower blood pressure by blocking adrenaline. Also known as beta-adrenergic blocking agents, they’re used for high blood pressure, irregular heartbeats, and after heart attacks. But not all beta-blockers are created equal—some are safer than others, especially for long-term use or if you have other health issues.
What makes a beta-blocker "safe"? It’s not just about avoiding side effects. It’s about matching the drug to your body. metoprolol, a cardioselective beta-blocker that mainly targets the heart is one of the most commonly prescribed because it rarely affects the lungs, making it safer for people with asthma or COPD. bisoprolol, another cardioselective option with a long half-life works just as well but only needs one daily dose, which helps people stick to their regimen. Both are preferred over older, non-selective beta-blockers like propranolol, which can cause fatigue, cold hands, or breathing trouble in sensitive patients.
Why does this matter? Because taking the wrong beta-blocker can lead to problems you didn’t expect—like worsening diabetes control, masking low blood sugar symptoms, or triggering depression in some users. That’s why doctors now start with the gentlest options first. If you’re on a beta-blocker and feel unusually tired, dizzy, or short of breath, it might not be your condition—it could be the drug. The safest beta-blockers are the ones that do their job without stepping on other systems in your body. You’ll find posts here that compare these drugs side by side, explain why some are better for older adults, and warn about hidden interactions with other meds like antidepressants or asthma inhalers. These aren’t just drug lists—they’re real-world guides from people who’ve been there.
Below, you’ll see real comparisons of beta-blockers with other heart meds, how they stack up against newer alternatives, and what to watch for if you’ve been on one for years. No fluff. Just what works, what doesn’t, and what your doctor might not tell you unless you ask.
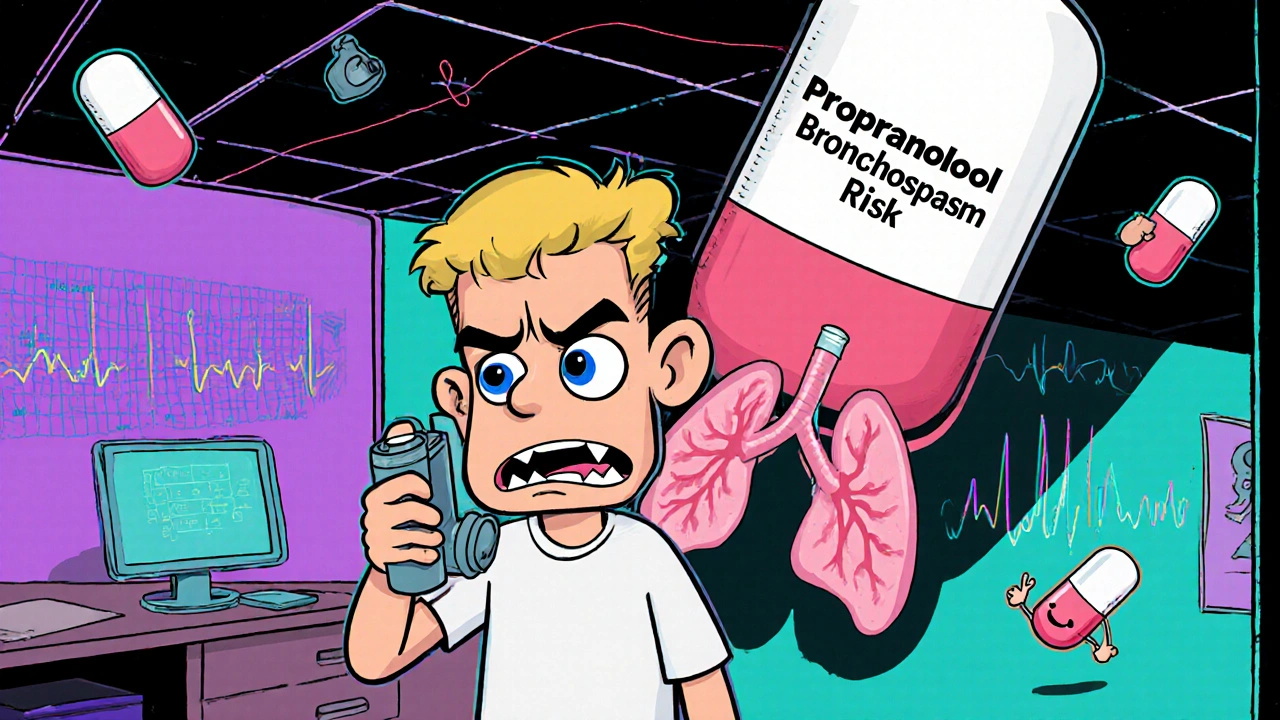
Beta-Blockers and Asthma: What You Need to Know About Bronchospasm Risks and Safer Choices
Beta-blockers were once banned for asthma patients due to bronchospasm risks. New evidence shows cardioselective options like atenolol and bisoprolol are safe for many, offering heart protection without triggering asthma attacks.